Multi-Factor Authentication, or MFA, currently infiltrates virtually every aspect of our digital lives. It is a protective shield helping to guard our private data, financial information and other proprietary details. Accessing social media, your bank, your email or your digital medical record app will more often than not require MFA before you can be admitted. But what is multi-factor authentication, and how does it work? ClearFuze handles managed IT services and IT data security for a number of Los Angeles businesses. Below we’ll dive into the details on MFA, the factors utilized and the various types available for adoption by your company.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat Is Multi-Factor Authentication?
At the heart of multi-factor authentication is protection for the digital user. Are you who you say you are? MFA provides real-time checks and balances to ensure the right people are accessing their own info. Take a look at this image from the National Institute of Standards and Technology:
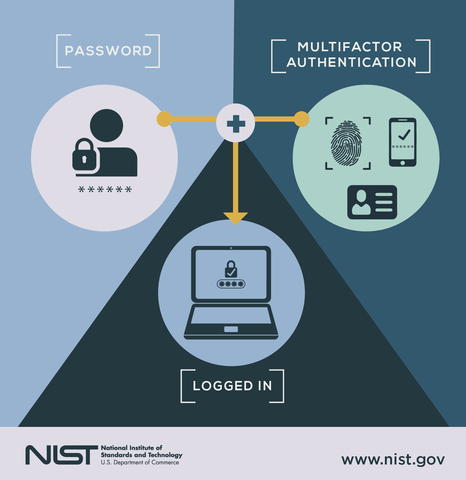
MFA in combination with a password and device recognition means you and your work can remain extremely safe. In fact, multi-factor authentication is one of the top three methods utilized by cybersecurity experts to protect their data online, according to this Google survey.
The Factors Used in Multi-Factor Authentication
There are three primary categories, or “factors,” used in multi-factor authentication. The factor will either be:
- Something that the user knows (knowledge)
- Something the user has (information)
- Something the user is (biometric)
Examples of Something Known By the User:
This factor—what a person knows—is the most commonly used. That being said, it is also the most vulnerable to hacking, since passwords can be stolen or shared unintentionally.
- A password
- A PIN (series of numbers)
- Answers to standardized questions (“Where did you go to elementary school?”)
Examples of Something Possessed By the User:
Possession factors can be likened to a lock that fits into a key. Although they have since grown more complex, the basic idea remains the same.
- A customized app
- Text message with a code
- Software or hardware token
- Security badge
Examples of Something Inherent To the User:
Biometric authentication refers to physical characteristics which cannot be replicated by other users. This makes biometric methodology an extremely secure choice.
- Fingerprint
- Palm print
- Voice recognition
- Retina and iris patterns
- DNA
There are two other factors sometimes used for MFA: location factors (based on where someone is,) and behavior factors (completing a puzzle or typing numbers in a particular order.) Sometimes technology limits which factors can be utilized, or a business will combine factors to make their data uniquely secure. Any number of combinations is possible here.
Types of Multi-Factor Authentication
2FA or 2-Factor Authentication: 2FA offers an additional level of security for the user. Think of it as one step beyond a password; once the password is entered and accepted, another layer of information is then required. 2FA is increasingly common these days because of an accompanying rise in cybercrime. All 2FA methods are not made equal. Some of the options listed above are far more secure than others.
3-Factor Authentication: Three-factor authentication translates into three levels of identity-confirming credentials—all taken from different “factor” groups. To enter a medical facility, for example, you may have to enter a pin, scan your retina, and wear a security badge. Going from 2FA to 3FA dramatically increases security.
4-Factor Authentication: Four-factor authentication is more rare but required within industries where data must be well-protected. Typically 4FA combines a possession, location, biometric, and a knowledge factor.
Cybersecurity Protection for Los Angeles Companies with ClearFuze
Multi-factor authentication is only one of many options available to LA business owners for securing their data. Its implementation can also vary according to your proprietary hardware, apps, networks, and systems of choice. Finally, MFA decisions come with a wide range of installation and support costs. What will you choose—and do you have expert assistance for training and maintenance?
Let ClearFuze help with the time-consuming details so that you can focus on the business at hand. Contact us today for a free consultation on our comprehensive cybersecurity offerings.




